Bimonthly assessment _MARCH
UTI with cirrhosis of liver with portal hypertension
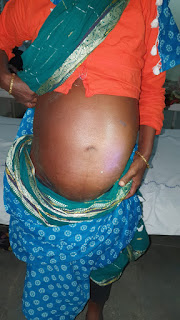
About his superficial abdominal veins :
For a long term alcoholic, he could be a risk factor to develop portal hypertension, which may be present with superficial abdominal veins and varices
Other differentials include:
Caput medusae due to portal hypertension
Dilated veins in IVC
Congenital
Obstruction of IVC
The etiology of the disease in this patient could be a chronic history of alcoholism. Chronic smoking leading to his apthous ulcers.
Based on his clinical finding there could be portal hypertension which could have been preceeded by cirrhosis of liver which might have been caused due to chronic alcoholism.
Cirrhosis of liver leads to reduced protein synthesis thereby leading to decreased serum albumin levels causing hypoalbuminemia.
patients with cirrhosis, synthesis is decreased because of the loss of hepatic cell mass. Also, portal blood flow is often decreased and poorly distributed, leading to maldistribution of nutrients and oxygen. The flow of substrate may affect certain functions of the liver, including protein synthesis, which is decreased in patients with cirrhosis who lack ascites. Albumin synthesis may actually increase in patients with cirrhosis who have ascites, possibly because of a change in hepatic interstitial colloid levels, which may act as an overriding stimulus for albumin production.
https://www.medscape.com/answers/166724-41451/how-does-cirrhosis-cause-hypoalbuminemia#qna
Yes
Inflammation and infection
Albumin is considered a negative acute phase reactant, which means that as inflammation and other acute physiologic processes occur, its levels decrease
In liver disease:Albumin is synthesized in the liver, and low serum albumin can be indicative of liver failure or diseases such as cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis. If present, hypoalbuminemia is generally considered to be a sign of advanced hepatic cirrhosis, or irreversible damage to the liver
Malnutrition or malabsorption
Low albumin levels can also indicate chronic malnutrition from protein losing enteropathy.[3] This is often caused or exacerbated by ulcerative colitis,[10] but can also be seen in cardiac disease and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conditions with severe hypoalbuminemia and no pedal edema- There can be a compensatory synthesis of protiens (globulins) other than albumin and thereby maintain the oncotic pressure in the intravascular compartment and preventing the extravasation of fluid. This could also be possible if there is a hypovolemic state in the same patient with hypoalbuminemia so that the pressures are again maintained and there is no fluid accumulation.
It is possible for one with hereditary analbuminemia to not have pedal edema. Since it is a chronic and hereditary disease there can be compensatory synthesis of other plasma proteins.
Ans: tamsulosin efficacy in UTI patients
1.α1-Adrenergic receptor antagonists are used by 80% of physicians as the first agent to treat patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) presenting with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS); 27 of 30 clinical trials have confirmed that α-blockers are effective for BPH treatment.
2.Tamsulosin's α1A subtype adrenergic receptor selectivity is considered to be responsible for its low cardiovascular side effects and lack of interaction with antihypertensives.
3.A 4-year extension, multicenter, open-label, phase IIIB clinical study evaluated long-term efficacy, safety, and tolerability of tamsulosin for up to 6 years; the study found a consistent statistically significant improvement in AUA symptom scores over 6 years, and most patients showed improvement during the first year that was sustained over 6 years.
4.The low incidence of acute urinary retention in patients treated with tamsulosin for up to 6 years suggests that tamsulosin may reduce the risk of AUR in patients with BPH.
5.Response to treatment and incidence of adverse events (eg, rhinitis and abnormal ejaculation) in patients with hypertension, diabetes, or nonhypertensive cardiovascular disease did not differ significantly from that in those without.
6.Abnormal ejaculation is an important side effect of tamsulosin, but it resulted in few discontinuations during treatment. It may not always be deemed important by patients, and was not linked to complaints of decreased libido, impotence, or other changes in sexual function.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1477608/
Nitrofurantoin efficacy:
Diuretics reduce right ventricular dilatation and improve its contractility and also reduce extravascular lung water . They should be used cautiously as they can cause intravascular volume depletion that may deprive the right ventricle of adequate pre-load to maintain a normal stroke volume. Moreover, accumulation of bicarbonate from diuretic therapy can worsen alveolar hypoventilation and hypercapnia. The latter can result fluid retention despite diuretic therapy. Treatment of chronic hypercapnia may therefore be as important as diuretics in ameliorating sodium retention.




Comments
Post a Comment