Monthly assessment _MARCH_M.NAVYA CHOWDARY
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
a). What is the problem representation of this patient and what is the anatomical localization for his current problem based on the clinical findings?How specific is his dilated superficial Abdominal vein in making diagnosis?
b) What is the etiology of the current problem and how would you as a member of the treating team arrive at a diagnosis? What is the cause of his hypoalbuminemia?Why is the SAAG low?
c)Will PT,INR derangement preceed hypoalbuminemia in liver dysfunction??Share reference articles if any!
d)What is the etiology of his fever and pancytopenia?
e)Can there be conditions with severe hypoalbuminemia but no pedal edema? Can one have hereditary analbuminemia and yet have minimal edema? Please go this article https://www.
f) What is the efficacy of each of the drugs listed in his current treatment plan
QUESTION 2
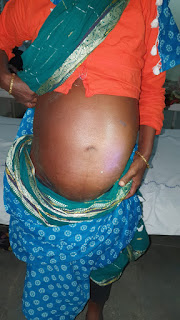
45year old female with abdominal distension
a). What is the problem representation of this patient and what is the anatomical localization for her current problem based on the clinical findings?
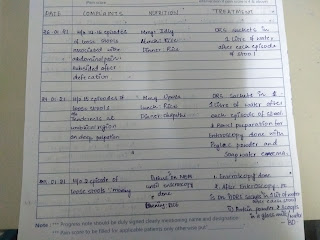
PROBLEM REPRESENTATION:
1.Abdominal distension since 2years
2.shortness of breath
3.pedal edema since 2 months
4.cachexia_malnourishment
Anatomical localisation:
1.abdominal distension : causes: fluid,fetus,flatus,fat,feaces
Here in this case:
O/E: flankfullness and fluid thrill is present __indicates distension is because of fluid_ASCITIS
In this case the pattern is ascitis followed by pedal edema _clinically it indicates problem is in liver.
2.shortness of breath and dull note in right side _IAA,ISA,IMA and decreased breath sounds on right side indicates pleural effusion .most likely in this case pleural effusion is due to her refractory ascitis _HEPATIC HYDROTHORAX.
3.Cachexia _ is due to her loss of appetite which in turn because of massive ascitis .
Overall the major problem in this case_refractory ascitis since 2 years.
b) What is the etiology of her refractory ascites and pleural effusion? and how would you as a member of the treating team arrive at a diagnosis?
Ans:
In this case ,ascitis recurs shortly after therapuetic paracentesis despite sodium restriction and diuretic treatment._refractory ascitis.
CAUSES OF REFRACTORY ASCITIS:
1.Non compliance to treatment
2.Tumor_hepatoma
3.Renal failure
4.spotaneous bacterial peritonitis
5.Portal vein thrombosis
6.NSAIDS
7.Infection
8.GI Bledding
On ascitic fluid analysis: It is high SAAG and low protein ,it probably due to portal hypertension.
she is on diuretics,frequent therapeutic paracentesis
Her RFT was normal _no renal failure,
Noincreased cell counts in ascitic fluid, no features of infection _rule out SBP
No H/O 7se of NSAIDS
On CECT abdomen_ no tumors identified in liver
No symptoms of GI bleeding:melena,hemetemesis.
So in this case most probably ascitis due to portal hypertension :
DD: cirrhosis of liver
Schistosomiasis
Portal vein outflow obstruction.
Cirrhosis is ruled out clinically no symptoms like jaundice,no coagulation disorders,no other signs of liver cell failure radiologically no altered echotexture,no shrunken liver,no nodules .
Stool microscopy was done to rule out schistosomiasis.
Portal vein thrombosis evaluation done by triple phase cect followed byMR Venogram.
On triple phase CECT :Focal short segment of intrahepatic segment of IVC just below the diaphragm with normal hepaticveins And multiple osteosclerotic lesions in pelvis,ribs,vertebral bodies __sarcoidosis /metastasis.
MR Vengram_ suggested severe narrowing of intrahepatic portion of IVC___Chronic buud chiari syndrome.
PLEURAL EFFUSION:
When pleural and Ascitic tap done on same time sent for analysis _both looks like almost same _both are transudates:so, pleural effusion is most likely due to Hepatic hydrothorax.
DD: 1.sarcoidosis:
2.tuberculosis: pleural fluid and sputum for AFB and CBNAAT was negative.clinically no h/o TB.
3.Malignancy: pleural fliuid cytology was normal ,no dysplastic cells
c) Approach to a patient with ascites?Clinically is there any way to differentiate pre hepatic, post hepatic and hepatic causes?
Ans:
d)Causes of budd chiari syndrome?Why did the patient undergo bone biopsy?
Ans:
Hypercoagulable states:
Inherited : Anti thrombin deficiency, Protein c deficiency,protein S deficiency,Factor v leiden mutation, prothrombin mutation
Acquired :Myeloproliferative disorders,PNH,Anti phospholipid syndrome,cancer,pregnancy,ocp use
Uncommon causes: HCC,RCC,Adrenl carcinoma
Misc: Aspergillosis,behcet syndrome,IVC webs,trauma,IBD,systemic sarcoidosis.
IN THIS CASE BONE BIOPSY DONE FROM POSTERIOR ILIAC CREST ON LEFT SIDE TO EVALUATE THE OSTEOSCLEROTIC LESIONS IN PELVIS , RIBS, VERTEBRAE .
d) Management strategies for refractory ascites and Budd chiari syndrome? Share the potential advantages and disadvantages of Peritoneal dialysis catheter placement in refractory ascites?
Ans:
Management of BCS:
1.Diagnosis of BCS made by clinical features, laboratory and radiological investigations , management of underlying cause
2.Anti coagulant therapy with LMWH and then warfarin aim for INR 2_3
3.Treat the complications of portal hypertension with spirinolactone ,furosemide,and gastroscopy for variceal screening and band ligation
4.consider angioplasty /stenting for venous obstruction
5.consider TIPS if no improvement with anticoagulation , angioplasty, stenting.
6.TIPS fails /no improvement and acute liver failure consider liver transplantation.
7.Monitor chronic BCS for HCC by 6 monthly USG and alpha fetoprotein.
Management of refractory ascitis :
Peritoneal dialysis catheter in refractory ascitis:
Advantages:
Heamodynamic stability
Ascitis control directly and in continuing fashion
Easy catheter placement
Disadvantages:
Protein loss
Over drainage of ascitis lead to hypotension
Dialysate leak or hydrothorax
Poor clearance owing to volume of ascitis
Higher infection risk .
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02975726
e) What is the efficacy of each of the drugs listed in his current treatment plan
Lasilactone
https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/907/smpc
Warfarin and LMWH:
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/184430-medication
f)What is the current outcome?and what could be the etiology of her current outcome?
Ans:
Patient got expired on14th of march preceded h/o vomiting and nausea
Cause of death was not confirmed, may be because of dislodgement of thrombus leading to pulmonary embolism.
QUESTION 3
55year old male with SOB and abdominal distension,orthopnea
a). What is the problem representation of this patient and what is the anatomical localization for his current problem based on the clinical findings?
b) What is the etiology of his ascites? and how would you as a member of the treating team arrive at a diagnosis?Chart out the sequence of events!
c)What is the efficacy of each of the drugs listed in his treatment plan?
d)What are his current outcomes ?
QUESTION 4
4)Please go through the thesis presentation below and answer the questions below by also discussing them with the presenter
a)What was the research question in the above thesis presentation?
b) What was the researcher's hypothesis?
c)What is the current available sensitivity and specificity of SAAG in diagnosis of etiology of ascites
5) Journal club questions on Ascites theme
a) Please identify the study design and outcomes in the article linked here https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.
b) Please download the CASP diagnostic study checklist here https://casp-uk.net/casp-
c) Please evaluate this randomized controlled trial on different techniques at ascitic tap here: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps




Comments
Post a Comment